Sub-Assemblies Introduction:
1. Magazine & Picture Frame Assembly
1.1.3D Model
-
Product Contact Parts - SS304
-
Product Non-Contact Parts - MS, RAL 7045
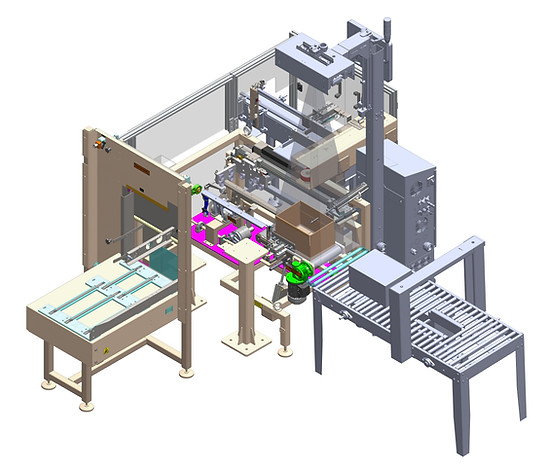
Magazine & Picture Frame
1.2.Magazine Assembly operation
-
The shippers will be loaded manually on the magazine.
-
Magazine is equipped with chain drive and motor. The magazine & picture frame assembly has two sensors to ensure it is loaded with shippers.
-
The photoelectric sensor and proximity sensors are used to detect the shipper's presence. The photoelectric sensor is used to detect the shippers at leading magazine and the proximity sensor with leaver mechanism is used to detect the shipper's backpressure at trailing magazine.
-
The leading magazine will get index when the case-erector robot is in shipper pick position, and the trailing magazine will get index until the proximity sensor detects the leaver.
-
The picture frame, which is attached with the magazine, is used to support the shippers and it will get adjusted according to height of the shippers by adjusting counter value and width will get adjusted by using knobs and leaver.
1.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions:
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
Always remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting/disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for magazine assembly.
1.4.Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
1.5. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
1.6 Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
2
1
1.
3
2.
3
2
4.
2
2.Case Erector Assembly
2.1. 3D Model
-
Product Contact Parts - SS304
-
Product Non-Contact Parts - MS, RAL 7045

2.2.Case Erector Assembly operation
-
Case Erectors is used to automatically form and fold shipper flaps by using pneumatic mechanism.
-
Case erector uses vacuum station-1 and 2 for holding the shipper and pneumatic cylinder assembly is used to close bottom minor and major flaps of the shipper. After forming shipper, it is transferred to the tilting conveyor by using linear shipper push cylinder. At tilting conveyor shipper will get loaded by using matrix pick and place robot.
Refer to the below video for the operation.

2.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Case Erector Assembly.
2.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
2.5. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
2.6. Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
1
1.
1
2.
1
4.
1
1
1
1
6
2
2
1
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
1
2
2
2
1
6
6
1
6
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
2
1
3.Case Erector Robot
3.1. 3D Model
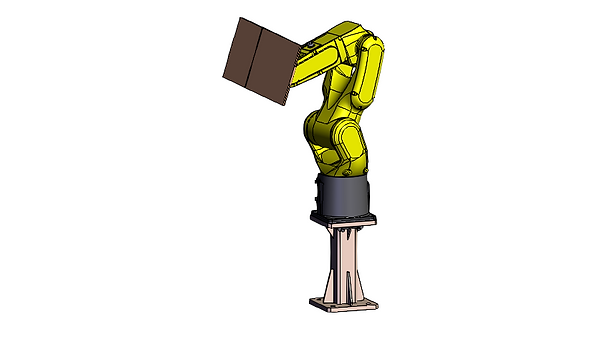
-
A case-erector robot (LR Mate 200iD) is used to pluck the shipper from the picture frame and place it over vaccum station-1, and after holding the shipper by vacuum cups, it will open the shipper and place it at vacuum station-2.
3.2. Case Erector Robot operation
Refer to the below video for the operation.

3.3 Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Robot/Cobot Assembly.
3.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
3.5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
3.6 Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
4
1.
1
2.
2
1
4.
2
1
6.
4.Modular Infeed Conveyor Assembly
4.1. 3D Model
-
Product Contact Parts - SS304
-
Product Non-Contact Parts - MS, RAL 7045

-
The function of Modular in-feed conveyor is to receive the bottles. The row of bottles is formed at the end of in-feed conveyor and this row of bottles conveyed to collation unit, the conveyor comprises photoelectric sensor inspection of bottles passing through and pneumatic stopper cylinder to stop the bottle flow while side shift of bottles by collation unit.
4.2 Modular Infeed Conveyor operation
Refer to the below video for the operation.

4.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Infeed Assembly.
4.4 Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
4.5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
4.6 Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
2
1.
1
2.
1
2
4.
2
6.
7.
1
1
2
2
1
5.Collation Unit Assembly
5.1. 3D Model
-
Product Contact Parts - SS304
-
Product Non-Contact Parts - MS, RAL 7045

-
The collation unit is used to form the matrix of bottles by side-shifting the bottles on the collation table. It has two servo motor-operated side shifting arms. It also has proximity sensors for the servo homing. The bottles on the infeed modular conveyor will be side-shifted and form the matrix; this matrix is piked by the bottle loader robot and placed into the shipper at the tilting conveyor.
5.2. Collation Unit operation
Refer to the below video for the operation.

5.3 Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Collation Unit Assembly.
5.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
5.5. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
5.6 Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
1.
1
2.
2
1
4.
2
2
6.Cobot for Matrix Pick & Place
6.1. 3D Model

-
The formed shipper will be transferred to the tilting conveyor, and it will be held by shipper hold cylinder and conveyor gets tilted.
-
The CRX 20iA Cobot will pick up the bottle matrix created at the collation unit and place it in the shipper, which is on the tilting conveyor.
-
This cobot has a pneumatically operated gripper, and the plates of the gripper will be changed manually as per the recipe change.
6.2. Matrix Pick and Place Cobot operation
Refer to the below video for the operation.

6.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Robot/Cobot Assembly.
6.4 Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
6.5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
6.6 Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
1.
1
2.
2
4.
2
6.
7.
1
1
2
2
2
8.
7.Taping Machine
7.1 3D Model
-
Product Contact Parts - SS304
-
Product Non-Contact Parts - MS, RAL 7045

-
The top and bottom taping machine is used to seal the shipper by using the top and bottom tape heads. The bottle loader robot will fill the shippers with bottles, and the filled shippers will be conveyed to the top and bottom taping machine.
-
The taping machine has the photoelectric sensors to sense top and bottom tape level and to detect shipper. After receiving the shipper from the tilting conveyor first top flaps will closed, and after that, the top and bottom tape will be applied, and the shipper will be transferred to the labelling conveyor.
-
The height and width of the taping machine will be adjusted manually by using the provided handle.
7.2. Taping machine operation
Refer to the below video for the operation.

7.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Taping Machine Assembly.
7.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
7.5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
7.6. Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
1.
2.
4.
1
13.
1
2
1
1
6
7.
9.
10.
11.
12.
2
1
2
2
2
1
2
1
8.Labelling Conveyor Assembly
8.1. 3D Model
-
Product Contact Parts - SS304
-
Product Non-Contact Parts - MS, RAL 7045

-
The flat belt labelling conveyor will receive the tapped shipper and convey it to the rollor infeed conveyor. It comprises shipper pusher cylinder to push the shipper on one side of the conveyor to ensure proper label will be applied on the shipper.
8.2. Labelling conveyor operation

Refer to the below video for the operation.
8.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for the labeling conveyor assembly.
8.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
8.5 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
8.6. Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
2
1
1.
2.
9.Label Applicator
9.1. 3D Model

Label Applicator
-
After applying tape to the shipper, it will be transferred to the labelling conveyor.
-
The label applicator applies the label to the rear corner of the shipper.
9.2. Label Applicator operation
9.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Label Applicator Assembly.
9.4. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
9.5. Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
3.
5.
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
1
1.
1
2.
1
1
4.
1
1
6.
10.Loop Closing Scanner
10.1. 3D Model
-
Main structure— MS with Zinc Plating

Loop Closing Scanner
-
The loop-closing scanner which is mounted at the label conveyor scans the label applied to the shipper. If the label is OK, then it will be placed on the accepted pallet, and if it is not OK, then it will be placed on the rejection pallet.
10.2. Loop Closing Scanner operation
10.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Scanner Assembly.
10.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
10.5. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
11.Palletizer Infeed Roller Conveyor
11.1. 3D Model
-
Product Contact Parts - SS304
-
Product Non-Contact Parts - MS, RAL 7045

-
After label applied to the shipper it will betransferred to the Palletizer infeed rollor conveyor and the shippers will be palletized by palletizer robot
11.2. Palletizer infeed roller conveyor operation
11.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Palletizer Infeed Roller Conveyor Assembly.
11.4. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
11.5 Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for details about Spare parts
Description
Consumables
Essential
Recomended
Sr No.
2
1
1.
1
2.
12.Palletizer Cobot
12.1. 3D Model

-
Palletizer Cobot (Fanuc CRX 25iA) will pick the shipper from the palletizer infeed roller conveyor and palletize according to the accepted and rejected signals.
-
The palletizer cobot has pneumatically operated pickhed
12.2. Palletizer Cobot operation
Refer to the below video for the operation.

12.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for robot/cobot assembly.
12.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
12.4. Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer to the below about the Troubleshooting.
13.Pallet Locator
13.1. 3D Model

Pallet Locator
-
Main Structure - MS, RAL 7045
-
Pallet Locator helps to load pallets at the correct location. Pallet locator has photoelectric sensors to detect pallet presence or absence.
13.2. Pallet Locator operation
14.Safety Scanner System
14.1. 3D Model

14.2. Safety Scanner operation
-
A safety laser scanner is a device designed to protect people from injury by detecting their presence and stopping machinery or hazards in the area.
14.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Scanner Assembly.
14.4. Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document.
15. Aggregation system
15.1. 3D Model

15.2. Aggregation operation
-
After the bottle matrix is placed into the shipper, the aggregation system scans the bottle matrix, and the result is shared with the palletizer cobot. Based on this information, the rejected shippers are placed on the rejection pallet.
15.3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
-
ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
-
ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
-
SAVE this manual for future reference.
-
DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
-
DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Click the below Maintenance Schedule for Aggregation Assembly.
16. Guards Assembly
16.1. 3D Model
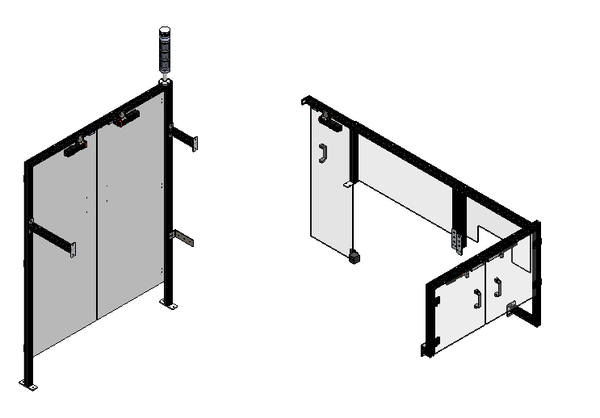
16.2. Guards operation
-
Guards cover the equipment and provide safety protection for operation of the equipment
